Mastering the Craft: The Basic 5 Skills of a Blacksmith
Blacksmithing, an ancient art form dating back centuries, continues to captivate artisans and enthusiasts alike with its blend of skill, creativity, and craftsmanship. At the heart of this age-old trade lie fundamental skills that every aspiring blacksmith must master. From shaping metal to creating intricate designs, the journey of a blacksmith is one of constant learning and refinement. In this post, we delve into the essential five skills that form the foundation of the blacksmithing craft.
Forging Techniques:
At the core of blacksmithing is the ability to forge metal. This skill involves heating metal to a malleable state and shaping it using various tools such as hammers, anvils, and tongs. Blacksmiths employ a range of forging techniques including drawing out, tapering, bending, twisting, and punching to achieve their desired designs. Mastery of these techniques allows blacksmiths to transform raw metal into functional pieces of art.
Heat Control:
A crucial skill for any blacksmith is the ability to control heat effectively. Different metals require specific temperatures for forging, and mastering heat control is essential to prevent the metal from becoming too brittle or soft. Blacksmiths use a combination of techniques such as adjusting the airflow in the forge, positioning the metal within the fire, and employing quenching methods to achieve the desired level of heat. Understanding the behaviour of metal under different temperatures is key to producing high-quality, durable pieces.
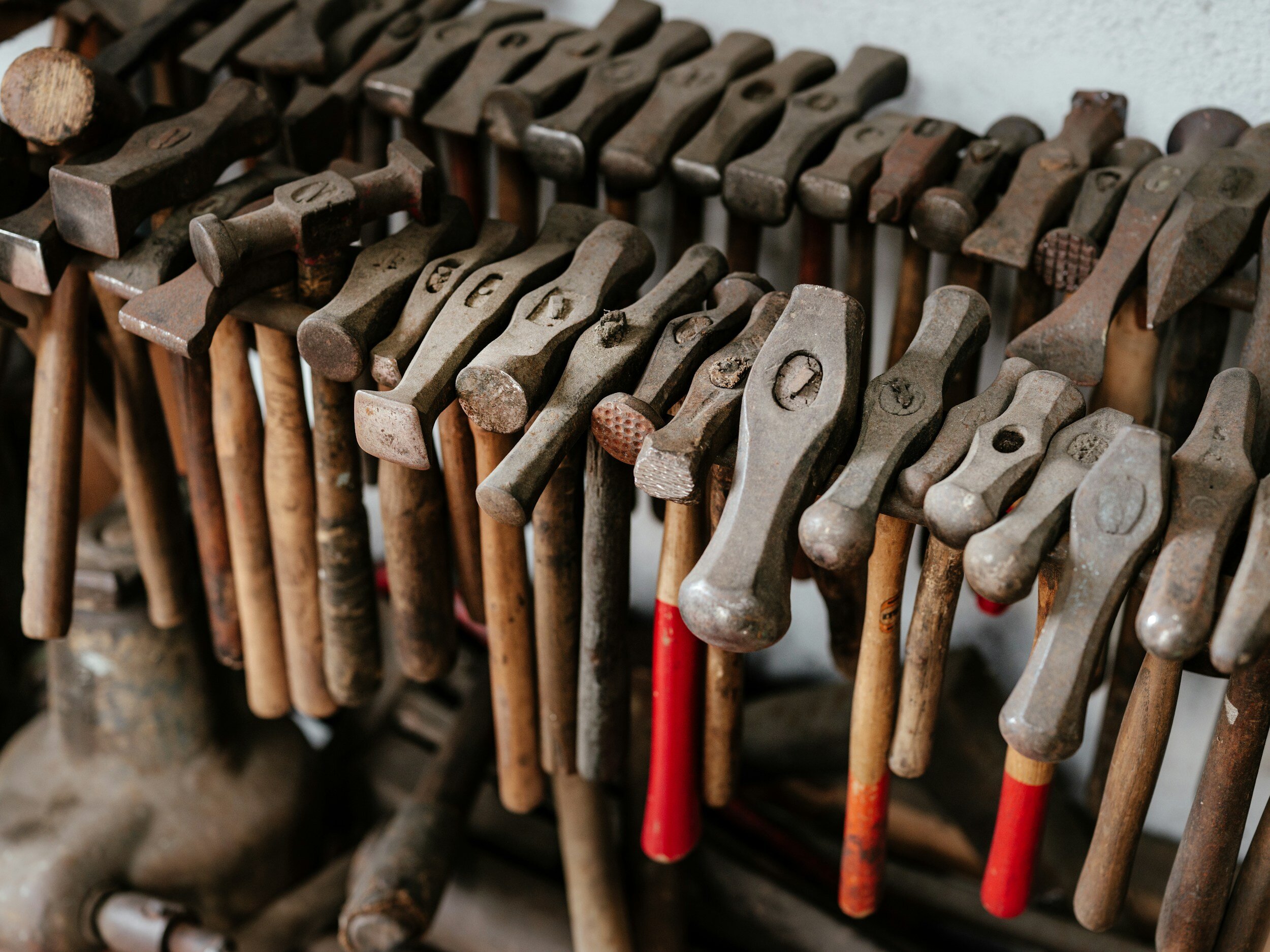
Tool Making and Maintenance:
Blacksmiths rely on a variety of specialised tools to carry out their work effectively. From forging hammers and chisels to tongs and punches, each tool plays a crucial role in the blacksmithing process. Learning to forge and maintain these tools is an essential skill for any blacksmith. Additionally, understanding the properties of different tool steels and how to heat treat them ensures that the tools remain sharp, durable, and reliable over time. A skilled blacksmith not only creates beautiful metalwork but also takes pride in crafting and caring for their tools.
Joinery and Welding:
Joinery is the art of joining pieces of metal together to create larger structures or assemblies. Traditional joinery techniques such as mortise and tenon joints, riveting, and forge welding are integral to blacksmithing. Mastering these techniques allows blacksmiths to fabricate complex assemblies with strength and precision. Forge welding, in particular, is a skill that requires careful control of heat and pressure to bond two pieces of metal into a single, seamless unit. Whether creating a sturdy gate or a delicate sculpture, proficiency in joinery is essential for bringing intricate designs to life.
Design and Creativity:
Beyond technical skill, creativity plays a vital role in the work of a blacksmith. From functional objects to ornamental pieces, blacksmiths have the opportunity to infuse their creations with their unique style and artistic vision. Developing an eye for design, understanding proportion and balance, and experimenting with different textures and finishes are all part of the creative process. Whether working on a custom commission or a personal project, the ability to translate ideas into tangible metalwork sets accomplished blacksmiths apart.
Mastering the craft of blacksmithing is a journey that requires dedication, patience, and a commitment to continuous learning. By honing the fundamental skills of forging, heat control, tool making, joinery, and creativity, blacksmiths can create timeless pieces that showcase both their technical expertise and artistic flair. Whether preserving traditional techniques or pushing the boundaries of innovation, the basic skills of a blacksmith form the cornerstone of this ancient craft, ensuring its legacy for generations to come.